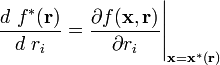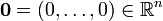Consider an arbitrary maximization (or minimization) problem where the objective function
 depends on some parameters
depends on some parameters 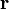 :
: is the problem's optimal-value function — it gives the maximized (or minimized) value of the objective function
is the problem's optimal-value function — it gives the maximized (or minimized) value of the objective function  as a function of its parameters
as a function of its parameters 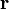 .
.Let
 be the (arg max) value of
be the (arg max) value of  , expressed in terms of the parameters, that solves the optimisation problem, so that
, expressed in terms of the parameters, that solves the optimisation problem, so that 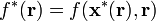 . The envelope theorem tells us how
. The envelope theorem tells us how  changes as a parameter changes, namely:
changes as a parameter changes, namely: with respect to ri is given by the partial derivative of
with respect to ri is given by the partial derivative of  with respect to ri, holding
with respect to ri, holding  fixed, and then evaluating at the optimal choice
fixed, and then evaluating at the optimal choice 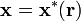 .
.[edit] General envelope theorem
There also exists a version of the theorem, called the general envelope theorem, used in constrained optimisation problems which relates the partial derivatives of the optimal-value function to the partial derivatives of the Lagrangian function.We are considering the following optimisation problem in formulating the theorem (max may be replaced by min, and all results still hold):
 is the dot product
is the dot product
 are treated as constants during differentiation of the Lagrangian function, then their values as functions of the parameters are substituted in afterwards.
are treated as constants during differentiation of the Lagrangian function, then their values as functions of the parameters are substituted in afterwards.